Traverse
源码 parse 成 AST 后,需要进行 AST 的遍历和增删改 ( transform ) .
Babel 会递归遍历 AST ,遍历过程中处理到不同的 AST 会调用不同的 visitor 函数来实现 transform 。
visitor 模式
visitor 模式 ( 访问者模式 ) 是 23 种经典设计模式中的一种。
当被操作的对象结构比较稳定,而操作对象的逻辑经常变化时,通过分离逻辑和对象结构,使得它们能独立扩展,这就是 visitor 模式的思想。
Element 和 Visitor 分别代表对象结构和操作逻辑,两者可以独立扩展,在 Client 里面组合两者,使用 visitor 操作 element,这就是 visitor 模式。
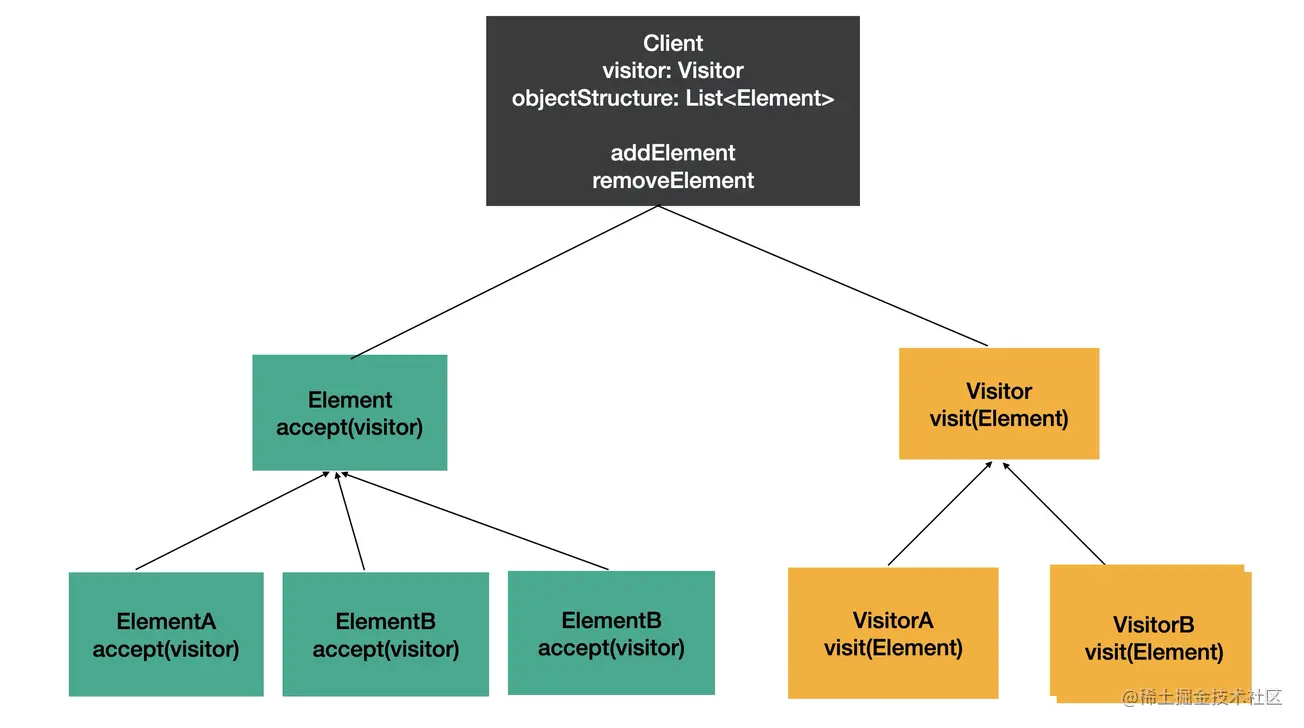
可以把要操作的对象看作公寓,每个字段看作一个房间,而房间内住的人就是 visitor 。
对应到 Babel traverse 的实现,就是 AST 和 visitor 分离,在 tarverse ( 遍历 ) AST 的时候,调用注册的 visitor 对其进行处理。
这样使得 AST 的结构和遍历算法固定,visitor 可以通过插件独立扩展。
路径和作用域
Babel AST 中只包含源码的一些信息,但是操作 AST 时要拿到父节点的信息,并且也需要对 AST 增删改的方法,这些都在 path 对象里。
Babel 会在 traverse 过程中在 path 里维护节点的父节点引用,在其中保存 scope ( 作用域 ) 的信息,同时也提供增删改 AST 的方法
path 的属性
path 有以下属性和方法
path {
// 属性:
node
parent
parentPath
scope
hub
container
key
listKey
// 方法
get(key)
set(key, node)
inList()
getSibling(key)
getNextSibling()
getPrevSibling()
getAllPrevSiblings()
getAllNextSiblings()
isXxx(opts)
assertXxx(opts)
find(callback)
findParent(callback)
insertBefore(nodes)
insertAfter(nodes)
replaceWith(replacement)
replaceWithMultiple(nodes)
replaceWithSourceString(replacement)
remove()
traverse(visitor, state)
skip()
stop()
}path {
// 属性:
node
parent
parentPath
scope
hub
container
key
listKey
// 方法
get(key)
set(key, node)
inList()
getSibling(key)
getNextSibling()
getPrevSibling()
getAllPrevSiblings()
getAllNextSiblings()
isXxx(opts)
assertXxx(opts)
find(callback)
findParent(callback)
insertBefore(nodes)
insertAfter(nodes)
replaceWith(replacement)
replaceWithMultiple(nodes)
replaceWithSourceString(replacement)
remove()
traverse(visitor, state)
skip()
stop()
}含义:
- path.node :当前 AST 节点
- path.parent :父节点
- path.parentPath :父 AST 节点的 path
- path.scope :作用域
- path.hub :可以通过 path.hub.file 拿到最外层 File 对象,path.hub.getScope 拿到最外层个作用域,path.hub.getCode 拿到源码字符串
- path.container :当前 AST 节点所在的父节点属性的属性值
- path.key :当前 AST 节点所在父节点属性的属性名或所在数组的下标
- path.listkey :当前 AST 节点所在父节点属性的属性值为数组时 listkey 为该属性名,否则为 undefined
因为 AST 节点要挂在父 AST 节点的某个属性上,那个属性的属性值就是这个 AST 节点的 container 。
如 CallExpression 有 callee 和 arguments 属性,那么对于 callee 的 AST 节点,callee 的属性值就是它的 container ,而 callee 就是它的 key 。
BlockStatement 有 body 属性,是一个数组,对于数组中的每一个 AST 来说,这个数组就是它们的 container ,而 listkey 是 body ,key 是下标。
path 的方法
- inList() :判断节点是否在数组中,如果 container 为数组,也就是有 listkey 的时候,返回 true
- get(key) :获取某个属性的 path
- set(key, node) :设置某个属性的值
- getSibling(key) :获取某个下标的兄弟节点
- getNextSibling() :获取下一个兄弟节点
- getPrevSibling() :获取上一个兄弟节点
- getAllPrevSiblings() :获取之前的所有兄弟节点
- getAllNextSiblings() :获取之后的所有兄弟节点
- find(callback) :从当前节点到根节点来查找节点 ( 包括当前节点 ) ,调用 callback ( 传入 path ) 来决定是否终止查找
- isXxx(opts) :判断当前节点是否是某个类型,可以传入属性和属性值进一步判断,比如
path.isIdentifier({ name: "a"}) - assertXxx(opts) :同 isXxx ,但不返回布尔值,而是抛出异常
- insertBefore(nodes) :在之前插入节点,可以是单个节点或者节点数组
- insertAfter(nodes) :在之后插入节点,可以是单个节点或者节点数组
- replaceWith(replacement) :用某个节点替换当前节点
- replaceWithMultiple(nodes) :用多个节点替换当前节点
- replaceWithSourceString(replacement) :解析源码成 AST ,然后替换替换当前节点
- remove() :删除当前节点
- traverse(visitor, state) :遍历当前节点的子节点,传入 visitor 和 state ( state 是不同节点间传递数据的方式 )
- skip() :跳过当前节点的子节点遍历
- stop() :结束所有遍历
path.scope 作用域
scope 是作用域信息,JavaScript 中能生成作用域的是模块、函数、块等,而作用域之间会形成嵌套关系,也就是作用域链。
Babel 在遍历的过程中会生成作用域链保存在 path.scope 中。
属性和方法如下:
path.scope {
bindings
block
parent
parentBlock
path
references
dump()
parentBlock()
getAllBindings()
getBinding(name)
hasBinding(name)
getOwnBinding(name)
parentHasBinding(name)
removeBinding(name)
moveBindingTo(name, scope)
generateUid(name)
}path.scope {
bindings
block
parent
parentBlock
path
references
dump()
parentBlock()
getAllBindings()
getBinding(name)
hasBinding(name)
getOwnBinding(name)
parentHasBinding(name)
removeBinding(name)
moveBindingTo(name, scope)
generateUid(name)
}含义:
- scope.bindings :当前作用域内声明的所有变量
- scope.block :生成作用域的 block
- scope.path :生成作用域的节点对应的 path
- scope。references :所有 binding 的引用对应的 path
- scope.dump() :打印作用域链的所有 binding 到控制台
- scope.parentBlock() :父级作用域的 block
- getAllBindings() :从当前作用域到跟作用域的所有 binding 的合并
- getBinding(name) :查找某个 binding ,从当前作用域一直查找到根作用域
- getOwnBinding(name) :从当前作用域查找 binding
- parentHasBinding(name, noGlobals) :查找某个 binding ,从父作用域查到根作用域,不包括当前作用域,可以通过 noGlobals 参数指定是否算上全局变量 ( 比如 console ,不需要声明就可用),默认 false
- removeBinding(name) :删除某个 binding
- hasBinding(name, noGlobals) :从当前作用域查找 binding ,可以指定是否算上全局变量,默认 false
- moveBindingTo(name, scope) :把当前作用域中的某个 binding 移动到其他作用域
- generateUid(name) :生成作用域内唯一的名字,根据 name 添加下划线,比如 name 为 a ,会尝试生成 _a ,如果被占用会生成 __a ,直到生成没有被使用的名字
scope.block
能形成 scope 的有以下节点,这些节点也叫 block 节点。
export type Scopable =
| BlockStatement
| CatchClause
| DoWhileStatement
| ForInStatement
| ForStatement
| FunctionDeclaration
| FunctionExpression
| Program
| ObjectMethod
| SwitchStatement
| WhileStatement
| ArrowFunctionExpression
| ClassExpression
| ClassDeclaration
| ForOfStatement
| ClassMethod
| ClassPrivateMethod
| StaticBlock
| TSModuleBlockexport type Scopable =
| BlockStatement
| CatchClause
| DoWhileStatement
| ForInStatement
| ForStatement
| FunctionDeclaration
| FunctionExpression
| Program
| ObjectMethod
| SwitchStatement
| WhileStatement
| ArrowFunctionExpression
| ClassExpression
| ClassDeclaration
| ForOfStatement
| ClassMethod
| ClassPrivateMethod
| StaticBlock
| TSModuleBlock可以通过 path.scope.block 拿到所在块对应的节点,通过 path.scope.parentBlock 拿到父作用域对应的块节点。
一般情况下不需要拿到生成作用域的块节点,只需要通过 path.scope 拿到作用域的信息,通过 path.scope.parent 拿到父作用域的信息。
作用域中保存的是声明的变量和对应的值,每一个声明叫做一个 binding ( 绑定 ) 。
binding 有多种 kind ,代表不同的声明方式。
binding.identifier 和 binding.path 分别代表标识符的 AST 、整个声明语句的 AST 。
声明之后的变量会被引用和修改,binding.referenced 代表声明的变量是否被引用,binding.constant 代表变量是否被修改过。如果被引用了,就可以通过 binding.referencePaths 拿到所有引用的语句的 path 。如果被修改了,可以通过 binding.constViolations 拿到所有修改的语句的 path 。
path 的众多 api 正是 Babel 的强大所在。主要是操作当前节点、当前节点的父节点、兄弟节点、作用域,以及增删改的方法。
state
state 是遍历过程中 AST 节点之间传递数据的方式,插件的 visitor 中,第一个参数是 path ,第二个参数就是 state 。
插件可以从 state 中拿到 opts ,也就是插件的配置项,也可以拿到 file 对象,file 中有一些文件级别的信息,也可以从 path.hub.file 中拿。
可以在遍历的过程中在 state 中保存一些状态信息,用于后续的 AST 处理,不是遍历过程中的数据,可以通过 file.set 、file.get 保存。
AST 的别名
遍历的时候要指定 visitor 处理的 AST ,有的时候需要对多个节点做同样的处理,Babel 支持指定多个 AST 类型,也可以通过别名指定一系列类型。
// 单个 AST 类型
FunctionDeclaration(path, state) {},
// 多个 AST 类型
'FunctionDeclaration|VariableDeclaration'(path, state) {}
// AST 类型别名
Declaration(){} // 单个 AST 类型
FunctionDeclaration(path, state) {},
// 多个 AST 类型
'FunctionDeclaration|VariableDeclaration'(path, state) {}
// AST 类型别名
Declaration(){} Ayingotts's notes
Ayingotts's notes